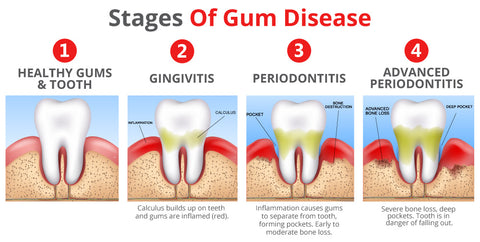
Inflammated gums are a common sign of gum disease. They swell and ulcerate and begin to lose the support of their teeth. In severe cases, the condition can result in tooth loss. Periodontitis is a chronic problem that can occur at any time in a person’s life. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is time to see a dentist. To learn how to prevent and treat this condition, keep reading this article.
Poor nutrition and lack of saliva production are also risk factors for gum disease. These factors result in impaired healing and increased plaque formation. Some medications, such as those for hypertension and diabetes, can also impair the body’s response to bacteria. Certain diseases, such as HIV or AIDS, can impair the immune system and make the body more susceptible to gum disease. If you’re taking any of these medications, you may be increasing your risk.
People with periodontal disease may be more prone to developing this type of infection. In most cases, this condition is easy to treat, but it can be extremely painful. During a routine dental exam, dentists will look for symptoms of gum infection. Swollen or bleeding gums may be a sign of gingivitis. Using a probe, you can detect foci of inflammation. X-rays cannot detect gingivitis because it does not affect the bone that supports the teeth.
Some medications reduce the production of saliva in the mouth. Antihistamines, birth control pills and antidepressants are known to reduce the amount of saliva in the mouth. In addition, genetics and other health conditions may put you at risk for developing periodontitis. If you have an autoimmune disease, this condition can lead to other problems. This will ultimately lead to tooth loss. Therefore, it is important to visit your dentist regularly for regular checkups.
When gum disease occurs, it causes pain in the mouth. Patients with gum disease are more likely to bleed when brushing or flossing their teeth, which is a symptom of a gum infection. Fortunately, gum disease is completely preventable. By following these steps, you can prevent and even reverse this disease. Although periodontal disease is a common condition, it is important to seek medical attention from a dentist to avoid serious complications. There are many factors that can contribute to periodontal disease. You can learn more about this on the website iHealzy.
There are several factors that can affect gum health. Many of these have to do with your diet, such as your sugar intake or physical activity level. Some of these factors may increase your risk of developing periodontitis. Infections in the mouth can lead to abscesses and tooth loss. In severe cases, the infection can even spread to the jawbone and even to the heart. If you have diabetes, you need to visit your dentist regularly.
Infections can lead to a pocket of pus called an abscess. These infections require prompt treatment to prevent further damage. Advanced periodontitis can affect the root structure of a tooth and require surgery. It can even affect other organs, such as the kidneys and the liver. If untreated, this infection can lead to tooth loss and jaw bone problems. There are many symptoms of periodontitis.
In some cases, the gum disease can be triggered by medication. Some drugs, such as birth control pills, suppress the production of saliva. These medicines can also cause periodontitis. In addition to the medications that lower saliva production, genetics and diseases that inhibit the immune system may also lead to periodontitis. Inflammation of gum tissue can cause it to be infected and can even cause tooth loss. As with any infection, it is important to get treatment as soon as you notice any of these symptoms.
The best way to prevent periodontal disease is to maintain good oral hygiene. Proper dental care and brushing twice a day are essential. Flossing is necessary to remove plaque and toxins that cause periodontitis. To prevent periodontal disease, you must visit a dentist regularly. The best way to stop this disease from progressing is to follow proper care and prevention. There are several signs of this condition.