The main causes of varicose veins are activities that put pressure on the legs, such as running, walking, or squatting. A number of other factors can increase the risk of developing these veins, including pregnancy, sedentary work, and chronic constipation. In addition, certain diseases or lifestyle habits can aggravate the problem, including obesity. Women should also avoid activities that cause direct cuts to their legs, as this can lead to more bleeding than normal.
There are several causes of varicose veins. Age, heredity, and gender are not major risk factors for the development of these conditions. Those with high blood pressure and standing jobs are also more likely to develop them. Another risk factor is pregnancy, which causes the body to store more blood and place extra pressure on the circulatory system. Changes in hormone levels during pregnancy may also relax the blood vessel walls and increase the risk of varicose veins.
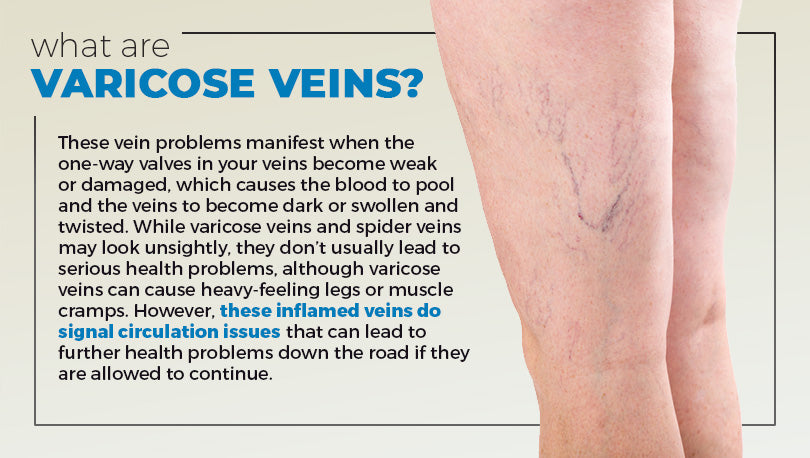
The primary cause of varicose veins is blood flow. The damaged valves and walls cause blood to pool and flow backwards, resulting in varicose veins. The condition may affect any age group and is more common in women than men. Many people have no symptoms, but it can be embarrassing for people to have. Symptoms can include aching and pain behind the knees. If left untreated, varicose veins can lead to ulcers and skin discoloration.
Some other causes of varicose veins are hormonal changes or the use of hormonal pills. Female hormones relax the venous wall, making them more susceptible to blood pooling. Moreover, trauma, blood clots, or pelvic tumors can cause the valves to rupture and enlarge. However, these factors do not cause the condition to worsen. There is no single treatment for varicose veins.
Other causes of varicose veins include pregnancy, aging, and genetics. Some types of varicose veins may develop because of genetics. Some may have no symptoms while others will develop after pregnancy. One of these causes is age. Those who are older are more likely to suffer from this disorder than others. Those who suffer from the disease can also experience painful leg ulcers.
Symptoms of varicose veins can be embarrassing and cause other health problems. Some people may experience no symptoms at all. In this case, treatment is needed if the condition worsens and you are not satisfied with the appearance of your legs. There are many options for treating varicose veins. If you are experiencing a lot of discomfort or swollen ankles, you should see a doctor.
In addition to age, obesity and heredity, there are other factors that can lead to varicose veins. If you are overweight, you may also develop varicose veins. These conditions are common in women and are treatable with the right treatment. If diagnosed early, these veins can be easily removed on their own, and they can even be prevented by treating them with medication. You should see your doctor for a thorough examination as they can lead to serious complications.
The main causes of varicose veins vary from person to person. Generally, age is the main reason. Being born with weak venous valves increases the risk. Having a family member with this disease increases the risk of developing varicose veins. There are other factors that can lead to varicose veins, such as hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
The main causes of varicose veins are genetic and hormonal factors. Neither age nor gender are factors in the development of the disease. A person’s blood pressure and heredity are two other major causes of varicose veins. Some people are born with this problem or may develop it later in life. Fortunately, in most cases, varicose veins are treatable. A doctor may also prescribe a cream Varix to help relieve the pain and discomfort caused by the condition.
The main cause of varicose veins is poor circulation. This can cause a number of complications, but is often a cosmetic problem. Some women with poor circulation are at higher risk for this condition. Other factors that increase the risk of developing varicose veins are smoking and pregnancy. Obese patients are also at greater risk. If their blood pressure is low, it will be more difficult for them to breathe.